| Kinase Assay: |
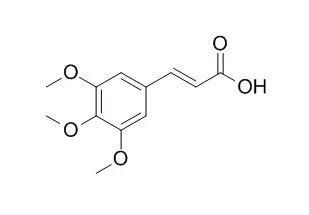
| Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Oct;36(10):1244-51. | | 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid (TMCA), one of the constituents of Polygalae Radix enhances pentobarbital-induced sleeping behaviors via GABAAergic systems in mice.[Pubmed: 23852644] | These experiments were performed to investigate whether 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid (TMCA), one of the constituents derived from Polygalae Radix, enhances pentobarbital-induced sleeping behaviors, and to alter sleep architecture through the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic systems in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid decreased the locomotor activity. 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid prolonged total sleep time, and reduced sleep latency induced by pentobarbital, similar to muscimol, a GABAA agonist. From the electrocencephalogram recording for 6 h after 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid administration, the number of sleep/wake cycles were reduced by 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid. 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid also increased the total sleep time and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. In addition, 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid increased Cl(-) influx in primary cultured cerebellar granule cells of mice. 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid increased the activation of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the expressions of γ-subunit of GABAA receptors in the cerebellar granule cells. However, α- and β-subunits proteins of GABAA receptors were not increased. Therefore,3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid would increase pentobarbital induced-sleep and NREM sleep in mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid may enhance sleep and alter sleep architecture through GABAAergic systyems. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2011;59(9):1178-9. | | A new hypoxia inducible factor-2 inhibitory pyrrolinone alkaloid from roots and stems of Piper sarmentosum.[Pubmed: 21881266 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new trimethoxycinnamoyl-2-pyrrolinone alkaloid, langkamide (1), along with the known compounds piplartine (2) and 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid (3) were isolated from the roots and stems of the shrub Piper sarmentosum ROXB. The structures were established by spectroscopic analyses and comparison of their spectral data with values reported in the literature.
CONCLUSIONS:
The compounds were tested for their ability to modulate hypoxia inducible factor-2 (HIF-2) transcription activity and all three showed HIF-2 inhibitory activity with EC₅₀ values of 14.0, 4.8, and 60.6 μM, respectively, for compounds 1, 2, and 3. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)