| In vitro: |
| Chem Biodivers. 2015 Jul;12(7):1057-67. | | Biological Evaluation of Secondary Metabolites from the Root of Machilus obovatifolia.[Pubmed: 26172326] | Bioassay-guided fractionation of the root of Machilus obovatifolia led to the isolation of four new lignans, epihenricine B (1), threo-(7'R,8'R) and threo-(7'S,8'S)-methylmachilusol D (2 and 3), and isofragransol A (4), along with 23 known compounds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were obtained as isomeric mixtures (i.e., 2/3 and 4/20, resp.). The structures were elucidated by spectral analyses. Among the isolates, 1, licarin A (12), Guaiacin (14), (±)-syringaresinol (21), and (-)-epicatechin (23) showed ABTS (=2,2'-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) cation radical-scavenging activity, with SC50 values of 11.7±0.5, 12.3±1.1, 11.0±0.1, 10.6±0.3, and 9.5±0.2 μM in 20 min, respectively. In addition, kachirachirol B (17) showed cytotoxicity against the NCI-H460 cell line with an IC50 value of 3.1 μg/ml.
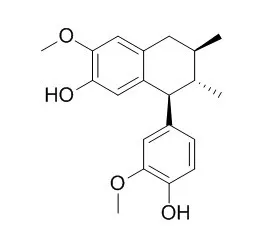
| | Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Apr;30(4):814-7. | | Stimulatory activity of lignans from Machilus thunbergii on osteoblast differentiation.[Pubmed: 17409528] | Phytoestrogens are naturally occurring compounds exerting estrogenic activity, and include isoflavonoids, flavonoids and lignans.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we evaluated the stimulating activity of six lignans, meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, machilin A, Guaiacin, isoGuaiacin and isoGuaiacin dimethylether, from Machilus thunbergii, on osteoblast differentiation employing primary cultures of mouse osteoblast as an in vitro assay system. Among the six lignans tested, arylnaphthalene type lignans such as Guaiacin, isoGuaiacin and isoGuaiacin dimethylether significantly increased alkaline phosphatase activity, whereas bibenzylbutane type lignans such as meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid, nordihydroguaiaretic acid and machilin A showed little effects. IsoGuaiacin and isoGuaiacin dimethylether also increased collagen synthesis as well as calcium deposition. In addition, treatment of the mouse osteoblasts with tamoxifen markedly reduced ALP activity increased by isoGuaiacin or isoGuaiacin dimethylether, suggesting the involvement of estrogen receptor in the action of these lignans on osteoblast differentiation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggest that arylnaphthalene type lignans such as Guaiacin, isoGuaiacin and isoGuaiacin dimethylether significantly increase osteoblast differentiation. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)