| Structure Identification: |
| Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009 Feb;44(2):154-7. | | Xanthones from leaves of Calophyllum inophyllum Linn.[Pubmed: 19408685] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To study the xanthones from the leaves of Calophyllum inophyllum Linn., several chromatography methods were employed to isolate the constituents. Investigation on the CHCl3 extract led to the isolation of a new xanthone named inophyxanthone A (1) and four known compounds, which were Pancixanthone A (2), gerontoxanthone B (3), jacareubin (4) and pyranojacareubin (5). Among them, compound 2 was obtained from this plant firstly, and compound 3 was obtained for the first time from this genus.
CONCLUSIONS:
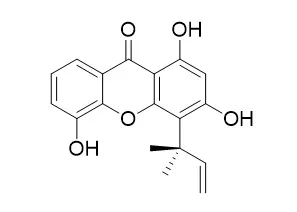
The structure of inophyxanthone A (1) was identified as 1, 3, 5-trihydroxy-2-(1, 1-dimethylallyl)xanthone by spectral analysis. | | Life Sci. 2004 Nov 5;75(25):3077-85. | | Antimalarial xanthones from Calophyllum caledonicum and Garcinia vieillardii.[Pubmed: 15474559 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antimalarial activity of 22 xanthones against chloroquino-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum was evaluated. Natural caloxanthone C (1), demethylcalabaxanthone (2), calothwaitesixanthone (3), calozeyloxanthone (4), dombakinaxanthone (5), macluraxanthone (6), and 6-deoxy-gamma-mangostin (7) were isolated from Calophyllum caledonicum. 1,6-dihydroxyxanthone (8), Pancixanthone A (9), isocudraniaxanthone B (10), isocudraniaxanthone A (11), 2-deprenylrheediaxanthone B (12) and 1,4,5-trihydroxyxanthone (13) were isolated from Garcinia vieillardii. Moreover, synthetic compounds (14-22) are analogues or intermediates of xanthones purified from Calophyllum caledonicum. The relationship between antimalarial activity and molecular structure of xanthones has also been explored.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most potent xanthones (2), (3) and (7) (IC50 = c.a. 1.0 microg/mL) are 1,3,7 trioxygenated and prenylated on the positions 2 and 8. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)